Outline
-
Introduction
-
What is Hyperthyroidism?
-
Importance of Recognizing Symptoms
-
-
Understanding Hyperthyroidism
-
What Causes Hyperthyroidism?
-
Who is at Risk?
-
-
Common Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
-
Increased Metabolism
-
Weight Loss
-
Rapid Heartbeat
-
-
Physical Symptoms
-
Tremors
-
Sweating
-
Muscle Weakness
-
-
Emotional and Mental Symptoms
-
Anxiety
-
Irritability
-
Difficulty Sleeping
-
-
Symptoms in Different Age Groups
-
Children
-
Adults
-
Elderly
-
-
Gender Differences in Symptoms
-
Symptoms in Women
-
Symptoms in Men
-
-
How Hyperthyroidism Affects Daily Life
-
Energy Levels
-
Cognitive Function
-
-
Complications of Untreated Hyperthyroidism
-
Heart Problems
-
Bone Issues
-
-
When to See a Doctor
-
Recognizing Serious Symptoms
-
Importance of Medical Diagnosis
-
-
Diagnosing Hyperthyroidism
-
Medical History and Physical Exam
-
Blood Tests
-
-
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
-
Medications
-
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
-
Surgery
-
-
Managing Symptoms Through Lifestyle Changes
-
Diet and Nutrition
-
Exercise and Stress Management
-
-
Living with Hyperthyroidism
-
Long-term Management
-
Support Systems
-
-
Conclusion
-
Summary of Key Points
-
Encouragement to Seek Help
-
Introduction
Hyperthyroidism, often referred to as an overactive thyroid, is a condition where the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. This hormone is crucial for regulating metabolism, heart rate, and many other bodily functions. Understanding and recognizing the symptoms of hyperthyroidism is essential for seeking timely treatment and managing the condition effectively.
Understanding Hyperthyroidism
What Causes Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism can be caused by several conditions, including Graves’ disease, thyroid nodules, and thyroiditis. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that results in the overproduction of thyroid hormones. Thyroid nodules are lumps in the thyroid gland that can produce excess hormone. Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid, which can cause hormone leakage.
Who is at Risk?
Hyperthyroidism can affect anyone, but it is more common in women and people over the age of 60. Family history, certain medical conditions, and excessive iodine intake can also increase the risk.
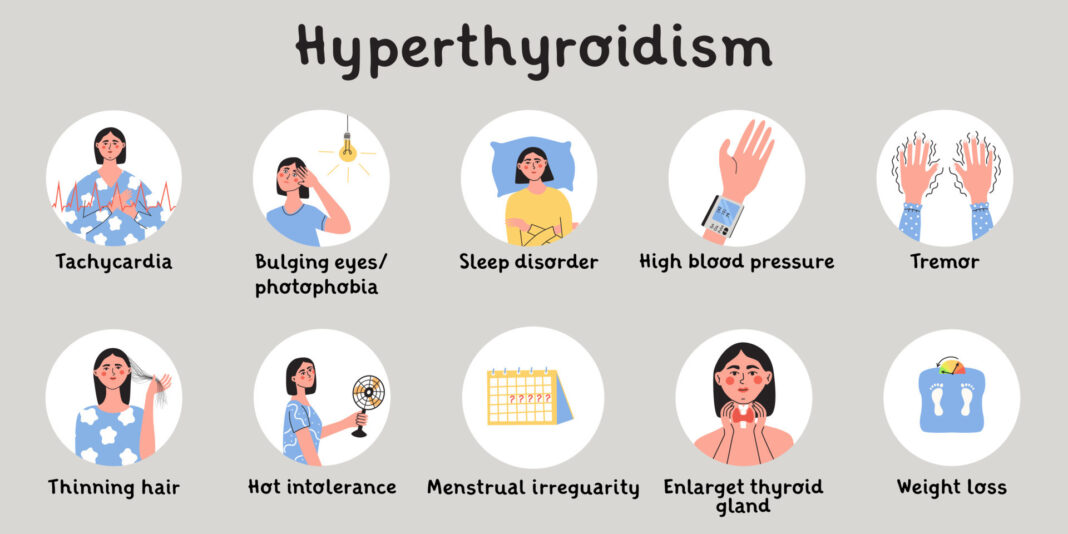
Common Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Increased Metabolism
One of the hallmark symptoms of hyperthyroidism is an increased metabolic rate. This can lead to various physical changes and sensations in the body.
Weight Loss
Despite an increased appetite, individuals with hyperthyroidism often experience unexplained weight loss due to the accelerated metabolism.
Rapid Heartbeat
A fast or irregular heartbeat, also known as palpitations, is another common symptom. This can be particularly noticeable during periods of rest or minimal activity.
Physical Symptoms
Tremors
Fine tremors in the hands and fingers are a typical physical sign of hyperthyroidism. These tremors can interfere with daily activities such as writing or holding objects.
Sweating
Excessive sweating and an intolerance to heat are also prevalent. This occurs because the body’s increased metabolism generates more heat.
Muscle Weakness
Muscle weakness, particularly in the upper arms and thighs, can be a challenging symptom. It may make simple tasks like climbing stairs or lifting objects difficult.
Emotional and Mental Symptoms
Anxiety
Hyperthyroidism often leads to heightened anxiety and nervousness. This can be overwhelming and impact one’s ability to relax and focus.
Irritability
Increased irritability and mood swings are also common. These emotional changes can strain relationships and daily interactions.
Difficulty Sleeping
Insomnia or difficulty sleeping is frequently reported by those with hyperthyroidism. The overactivity of the thyroid can make it hard to wind down and achieve restful sleep.
Symptoms in Different Age Groups
Children
In children, hyperthyroidism can lead to hyperactivity, poor school performance, and difficulty concentrating. It is crucial to address these symptoms early to avoid developmental issues.
Adults
Adults may experience a broader range of symptoms, including weight changes, fatigue, and mood disorders. These can significantly impact work and personal life.
Elderly
In the elderly, symptoms may be more subtle or attributed to aging. Common signs include unexplained weight loss, depression, and heart problems.
Gender Differences in Symptoms
Symptoms in Women
Women with hyperthyroidism may experience menstrual irregularities, such as lighter or less frequent periods. They are also at a higher risk for developing osteoporosis.
Symptoms in Men
Men may experience a decrease in libido, erectile dysfunction, and muscle weakness. These symptoms can be distressing and affect quality of life.
How Hyperthyroidism Affects Daily Life
Energy Levels
While some may feel an unusual burst of energy, it often comes with a crash leading to fatigue. This unpredictable energy level can make planning daily activities challenging.
Cognitive Function
Hyperthyroidism can affect cognitive functions, leading to issues with memory, concentration, and decision-making. This can impact work performance and personal responsibilities.
Complications of Untreated Hyperthyroidism
Heart Problems
If left untreated, hyperthyroidism can lead to severe heart issues, including atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeats) and congestive heart failure.
Bone Issues
Excess thyroid hormone can cause bones to thin, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
When to See a Doctor
Recognizing Serious Symptoms
If you experience severe symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or significant weight loss, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
Importance of Medical Diagnosis
A proper medical diagnosis is essential for managing hyperthyroidism. Only a healthcare professional can provide the necessary tests and treatment options.
Diagnosing Hyperthyroidism
Medical History and Physical Exam
A thorough medical history and physical exam are the first steps in diagnosing hyperthyroidism. Your doctor will look for signs such as an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) and tremors.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are used to measure levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Elevated T3 and T4 levels with low TSH indicate hyperthyroidism.
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
Medications
Antithyroid medications, such as methimazole and propylthiouracil, help reduce the production of thyroid hormones. Beta-blockers may also be prescribed to manage symptoms like rapid heartbeat.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
This treatment involves taking radioactive iodine orally, which destroys overactive thyroid cells. It is a common and effective method for treating hyperthyroidism.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland may be necessary. This is typically considered when other treatments are ineffective or not possible.
Managing Symptoms Through Lifestyle Changes
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet can help manage symptoms. Including foods rich in calcium and vitamin D is particularly important for bone health.
Exercise and Stress Management
Regular exercise and stress management techniques, such as yoga and meditation, can help improve overall well-being and reduce symptoms.
Living with Hyperthyroidism
Long-term Management
Managing hyperthyroidism is a long-term commitment. Regular check-ups and adherence to treatment plans are essential for maintaining health.
Support Systems
Having a support system, including family, friends, and support groups, can make managing hyperthyroidism easier. Sharing experiences and advice can provide emotional relief and practical tips.
Conclusion
Recognizing and understanding the symptoms of hyperthyroidism is crucial for early intervention and effective management. If you suspect you have hyperthyroidism, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. With the right approach, you can manage your symptoms and lead a healthy, active life.
FAQs
- Can hyperthyroidism go away on its own?
- In some cases, mild hyperthyroidism can resolve without treatment, but medical supervision is essential.
- What foods should I avoid if I have hyperthyroidism?
- It’s advisable to limit foods high in iodine, such as seaweed, and certain medications or supplements that contain iodine.
- Is hyperthyroidism genetic?
- There can be a genetic predisposition to hyperthyroidism, especially in autoimmune conditions like Graves’ disease.
- Can stress cause hyperthyroidism?
- While stress does not directly cause hyperthyroidism, it can exacerbate symptoms and trigger flare-ups.
- How long does it take to treat hyperthyroidism?
- Treatment duration varies; it can take several months to years, depending on the severity and chosen treatment method.