Outline
-
Introduction
-
What is Dyspraxia?
-
Importance of Understanding
-
-
What Causes Dyspraxia?
-
Genetic Factors
-
Neurological Factors
-
-
Symptoms
-
Early Childhood Symptoms
-
Symptoms in Adolescence
-
Adult Symptoms
-
-
Types
-
Motor
-
Verbal
-
Oral
-
-
Diagnosis
-
Initial Assessment
-
Comprehensive Diagnostic Tests
-
Professional Involvement
-
-
Living
-
Daily Challenges
-
Coping Strategies
-
Support Systems
-
-
Educational Strategies
-
Classroom Accommodations
-
Learning Techniques
-
Role of Teachers
-
-
Therapies and Treatments
-
Occupational Therapy
-
Speech and Language Therapy
-
Physical Therapy
-
-
Technological Aids
-
Assistive Technology
-
Apps and Tools
-
-
Impact on Mental Health
-
Emotional Challenges
-
Anxiety and Depression
-
-
Social Implications
-
Building Relationships
-
Social Skills Training
-
-
Success Stories
-
Notable Individuals
-
Overcoming Challenges
-
-
Support Networks
-
Family and Friends
-
Support Groups
-
Professional Help
-
-
Myths and Misconceptions
-
Common Myths
-
Fact-Checking
-
-
Conclusion
-
Recap of Key Points
-
Encouragement and Resources
-
-
FAQs
Introduction
What is Dyspraxia?
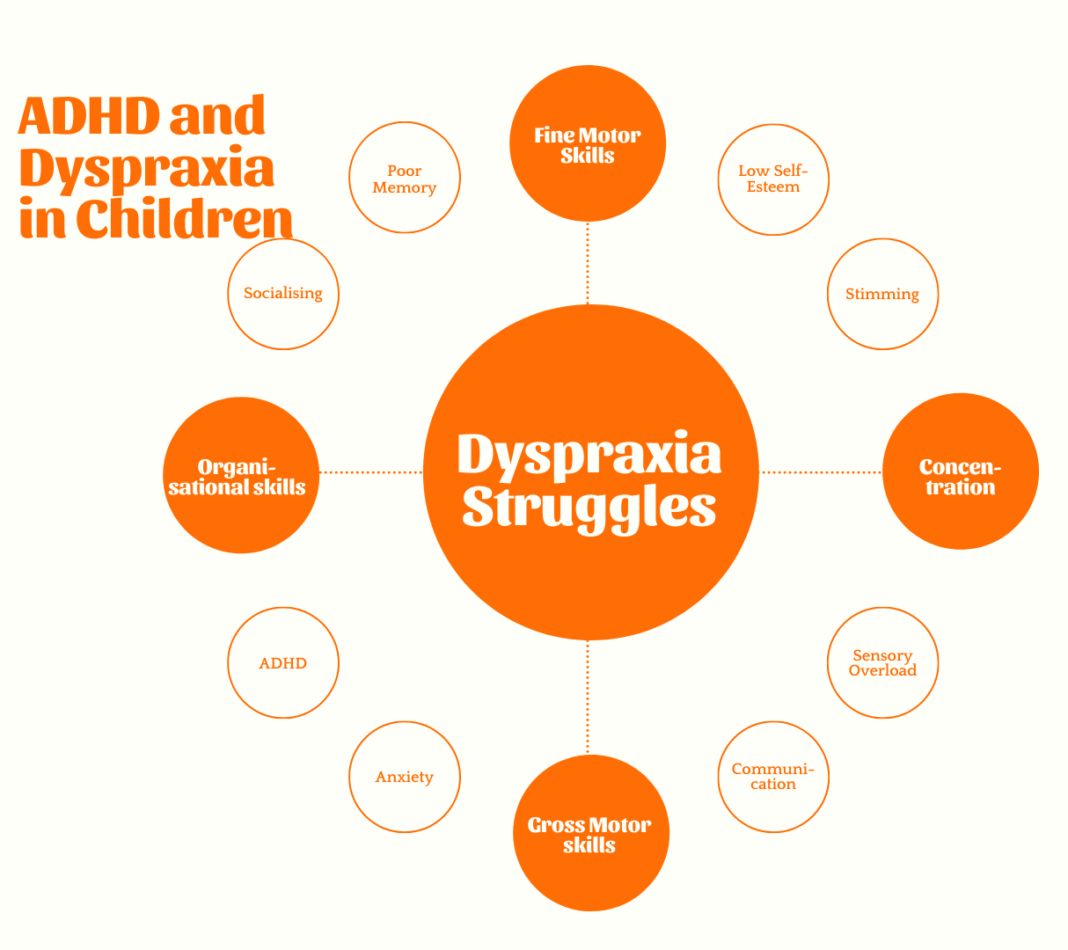
Dyspraxia, also known as Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD), is a neurological condition that affects physical coordination. Individuals with dyspraxia often struggle with tasks requiring balance, fine motor skills, and coordination, making daily activities challenging.
Importance of Understanding
Understanding dyspraxia is crucial for providing appropriate support and accommodations. Raising awareness helps create inclusive environments where individuals with dyspraxia can thrive and achieve their potential.
What Causes?
Genetic Factors
Research suggests that genetic factors play a role in dyspraxia. Family history can increase the likelihood of developing the condition, indicating a hereditary link.
Neurological Factors
Dyspraxia results from an issue in the way the brain processes information. It involves difficulties in the planning and execution of motor activities, often linked to atypical brain development.
Symptoms
Early Childhood Symptoms
In early childhood, dyspraxia symptoms include delayed developmental milestones such as crawling, walking, and speaking. Children may also struggle with hand-eye coordination and tasks like tying shoelaces or using utensils.
Symptoms in Adolescence
Adolescents with dyspraxia might experience difficulties with sports, handwriting, and organizational skills. They may have trouble following instructions and exhibit a lack of coordination in physical activities.
Adult Symptoms
In adults, dyspraxia can manifest as poor time management, difficulty driving, and challenges in workplace tasks. Adults may also experience emotional difficulties due to ongoing struggles with coordination and daily activities.
Types
Motor
Motor dyspraxia affects gross motor skills, such as running and jumping, as well as fine motor skills, like writing and buttoning a shirt.
Verbal
Verbal dyspraxia, also known as apraxia of speech, impacts the ability to coordinate the movements needed for speech. This can result in difficulty pronouncing words correctly and fluently.
Oral
Oral dyspraxia affects the movements required for eating, drinking, and speaking, making these everyday tasks challenging and sometimes uncomfortable.
Diagnosis
Initial Assessment
The initial assessment for dyspraxia typically involves observations and discussions with parents, teachers, and the individual. Early identification is crucial for implementing effective interventions.
Comprehensive Diagnostic Tests
Comprehensive diagnostic tests may include physical examinations, coordination tasks, and cognitive assessments to determine the extent of motor difficulties and rule out other conditions.
Professional Involvement
Diagnosing dyspraxia often requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving pediatricians, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and psychologists to provide a holistic understanding of the individual’s needs.
Living
Daily Challenges
Living with dyspraxia presents daily challenges, such as difficulty with routine tasks, social interactions, and academic or work-related activities. These challenges can impact self-esteem and independence.
Coping Strategies
Coping strategies for dyspraxia include breaking tasks into smaller steps, using visual aids, and practicing mindfulness techniques to manage stress and anxiety.
Support Systems
Support systems, including family, friends, and professionals, play a vital role in helping individuals with dyspraxia navigate their daily lives and overcome obstacles.
Educational Strategies
Classroom Accommodations
Classroom accommodations for students with dyspraxia can include additional time for tasks, use of assistive technology, and tailored learning materials to support their unique needs.
Learning Techniques
Effective learning techniques involve multisensory approaches, hands-on activities, and consistent routines to enhance comprehension and retention.
Role of Teachers
Teachers play a critical role in supporting students with dyspraxia by providing a structured environment, recognizing individual strengths, and fostering a positive learning atmosphere.
Therapies and Treatments
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on improving daily living skills, enhancing fine motor abilities, and developing adaptive techniques to increase independence.
Speech and Language Therapy
Speech and language therapy addresses verbal dyspraxia by working on speech patterns, pronunciation, and communication strategies to improve verbal interactions.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy aims to enhance gross motor skills, balance, and coordination through targeted exercises and activities.
Technological Aids
Assistive Technology
Assistive technology, such as voice-to-text software and specialized keyboards, helps individuals with dyspraxia perform tasks more efficiently and effectively.
Apps and Tools
Various apps and tools are designed to support organizational skills, time management, and motor coordination, providing practical assistance in everyday life.
Impact on Mental Health
Emotional Challenges
Dyspraxia can lead to emotional challenges, including frustration, low self-esteem, and feelings of inadequacy due to persistent difficulties with coordination and daily tasks.
Anxiety and Depression
The ongoing struggles associated with dyspraxia can contribute to anxiety and depression, highlighting the need for mental health support and counseling.
Social Implications
Building Relationships
Building relationships can be challenging for individuals with dyspraxia due to difficulties with social cues and coordination in group activities. It training can be beneficial.
Social Skills Training
Social skills training programs focus on developing effective communication, understanding social norms, and building confidence in social interactions.
Success Stories
Notable Individuals
Several notable individuals with dyspraxia have achieved significant success, including actors, athletes, and authors, serving as inspirations for others with the condition.
Overcoming Challenges
Personal stories of overcoming challenges illustrate the resilience and determination of individuals with dyspraxia, encouraging others to pursue their goals despite obstacles.
Support Networks
Family and Friends
Family and friends provide essential emotional support, encouragement, and practical assistance, creating a nurturing environment for individuals with dyspraxia.
Support Groups
Support groups offer a platform for sharing experiences, exchanging advice, and fostering a sense of community among individuals with dyspraxia and their families.
Professional Help
Professional help from therapists, counselors, and educators is vital for addressing the multifaceted needs of individuals and facilitating their development.
Myths and Misconceptions
Common Myths
Common myths about dyspraxia include misconceptions that it is simply clumsiness or that individuals with lack intelligence. Dispelling these myths is essential for raising awareness.
Fact-Checking
Fact-checking involves educating the public about the condition’s true nature, its impact on daily life, and the strategies that can support those affected.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
Dyspraxia is a complex neurological condition that affects coordination and daily functioning. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for providing effective support.
Encouragement and Resources
With the right support and resources, individuals with dyspraxia can lead fulfilling lives. Encouraging awareness and acceptance can help create more inclusive environments.
FAQs
What is the main cause?
It is primarily caused by issues in brain development that affect motor coordination, often influenced by genetic and neurological factors.
Can be cured?
There is no cure, but with appropriate therapies and support, individuals can manage symptoms and improve their coordination and daily functioning.
How is different?
While dyslexia are learning disorders, It primarily affects motor skills and coordination, whereas dyslexia impacts reading and language processing.
What are the best treatments?
Effective treatments for include occupational therapy, speech and language therapy, physical therapy, and the use of assistive technology to support daily tasks.
How can I support a loved one?
Supporting a loved one involves offering emotional support, encouraging their strengths, providing practical assistance, and advocating for appropriate accommodations.