Outline
- Introduction
- What is Lisinopril?
- Importance of understanding side effects
- What is Lisinopril?
- Brief overview
- Common uses
- How Does Lisinopril Work?
- Mechanism of action
- Benefits of Lisinopril
- Common Side Effects of Lisinopril
- Overview
- Frequency of common side effects
- Mild Side Effects
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Serious Side Effects
- Angioedema
- Kidney problems
- High potassium levels
- Liver issues
- Rare Side Effects
- Low blood pressure
- Increased risk of infection
- Severe allergic reactions
- Who Should Not Take Lisinopril?
- Contraindications
- Precautions
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Common drug interactions
- How to manage interactions
- Managing Side Effects
- When to seek medical help
- Lifestyle changes
- Medication adjustments
- Tips for Taking Lisinopril Safely
- Dosage recommendations
- Monitoring health
- Lisinopril and Pregnancy
- Risks during pregnancy
- Safe alternatives
- Patient Experiences
- Real-life stories
- Coping strategies
- FAQs about Lisinopril Side Effects
- Common questions
- Expert answers
- Conclusion
- Summary of key point
- Final thoughts
Introduction
Lisinopril side effects is a commonly prescribed medication used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. While it’s effective in managing these conditions, it’s crucial to understand the potential side effects to use it safely and effectively. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about Lisinopril side effects, from the mild to the severe, and how to manage them.
What is Lisinopril?
Lisinopril belongs to a class of medications known as ACE inhibitors. It helps relax blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood, which lowers blood pressure and reduces the strain on the heart. Doctors often prescribe it for conditions like hypertension and heart failure.
How Does Lisinopril Work?
Lisinopril works by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which is involved in producing a substance that tightens blood vessels. By blocking this enzyme, Lisinopril allows blood vessels to relax and widen, improving blood flow and lowering blood pressure. This mechanism also helps reduce the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
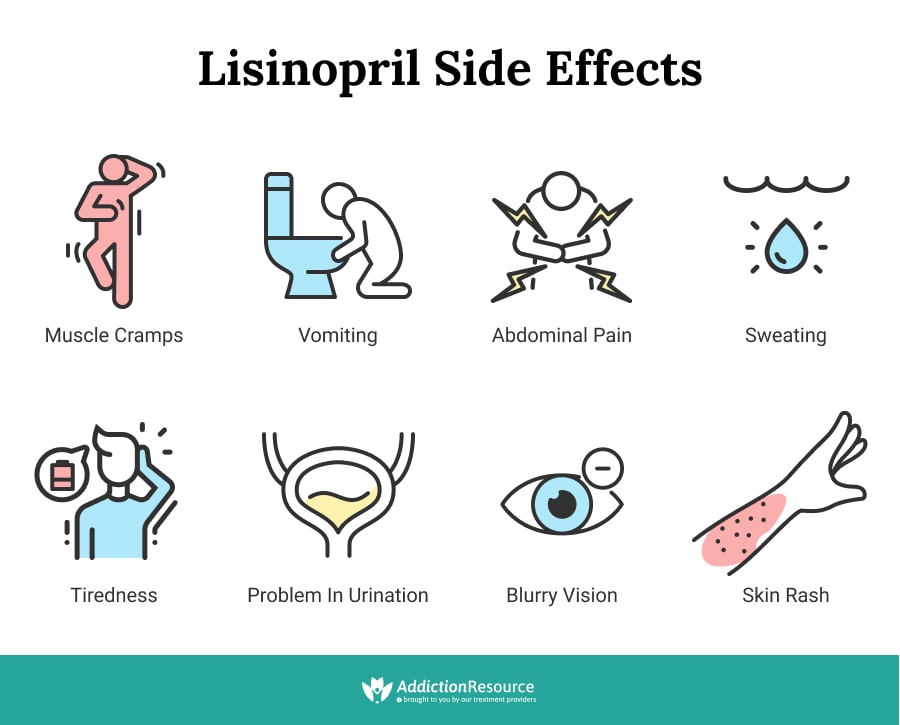
Common Side Effects of Lisinopril
While Lisinopril is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects. Most are mild and tend to resolve as your body adjusts to the medication. However, some can be more serious and require medical attention.
Mild Side Effects
- Headache
- Headaches are a common complaint among Lisinopril users. Staying hydrated and managing stress can help alleviate this side effect.
- Dizziness
- Feeling dizzy, especially when standing up quickly, is another common side effect. To minimize this, try standing up slowly and ensuring you’re adequately hydrated.
- Cough
- A persistent dry cough is a well-known side effect of ACE inhibitors like Lisinopril. If this becomes bothersome, consult your doctor about alternative medications.
- Fatigue
- Some people may feel unusually tired or fatigued when taking Lisinopril. This usually improves over time as your body gets used to the medication.
- Nausea
- Mild nausea can occur, particularly when starting the medication. Eating small, frequent meals can help manage this symptom.
Serious Side Effects
- Angioedema
- This is a rare but serious side effect that involves swelling of deeper layers of the skin, often around the eyes and lips. If you experience this, seek medical help immediately.
- Kidney Problems
- Lisinopril can affect kidney function, especially in people with preexisting kidney conditions. Regular monitoring of kidney function is recommended.
- High Potassium Levels
- Hyperkalemia, or high potassium levels, can occur and may cause heart problems. Symptoms include muscle weakness and irregular heartbeats.
- Liver Issues
- Though rare, Lisinopril can cause liver problems. Symptoms to watch for include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) and severe abdominal pain.
Rare Side Effects
- Low Blood Pressure
- Some individuals may experience significantly lowered blood pressure, leading to symptoms like fainting and dizziness. Regular monitoring and dosage adjustments can help manage this.
- Increased Risk of Infection
- Rarely, Lisinopril can affect white blood cell counts, increasing the risk of infections. Report any signs of infection, such as fever or sore throat, to your doctor.
- Severe Allergic Reactions
- Severe allergic reactions, though rare, can occur. Symptoms include rash, itching, and difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical attention if these occur.
Who Should Not Take Lisinopril?
Lisinopril is not suitable for everyone. People with the following conditions should avoid it:
- Pregnancy
- History of angioedema
- Severe kidney disease
- Allergic reactions to ACE inhibitors
Interactions with Other Medications
Lisinopril side effects can interact with several other medications, potentially causing harmful effects. Common interactions include:
- Diuretics
- Potassium supplements
- NSAIDs
- Other blood pressure medications
Always inform your doctor of all the medications you are taking to manage potential interactions effectively.
Managing Side Effects
If you experience side effects, there are several strategies to manage them:
- When to Seek Medical Help
- Seek immediate help for severe side effects like angioedema or signs of liver issues.
- Lifestyle Changes
- Adjust your diet, exercise regularly, and avoid alcohol to minimize side effects.
- Medication Adjustments
- Consult your doctor about adjusting the dosage or switching medications if side effects persist.
Tips for Taking Lisinopril Safely
- Dosage Recommendations
- Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage. Do not alter your dose without consulting your healthcare provider.
- Monitoring Health
- Regularly check your blood pressure and kidney function to ensure the medication is working effectively and safely.
Lisinopril and Pregnancy
Lisinopril is not recommended during pregnancy due to potential harm to the developing fetus. If you become pregnant while taking Lisinopril, consult your doctor immediately for safer alternatives.
Patient Experiences
Hearing from other patients can provide valuable insights. Many people manage Lisinopril side effects with lifestyle changes and by working closely with their healthcare providers.
FAQs
1. Can Lisinopril cause weight gain?
Weight gain is not a common side effect of Lisinopril. If you experience significant weight changes, consult your doctor.
2. How long do Lisinopril side effects last?
Mild side effects often improve within a few weeks. Serious side effects require medical attention and may persist until the medication is adjusted.
3. Can I drink alcohol while taking Lisinopril?
It’s best to avoid alcohol as it can enhance the blood pressure-lowering effects and increase dizziness.
4. What should I do if I miss a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it’s almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose. Do not double up.
5. Is it safe to take Lisinopril long-term?
Yes, many people take Lisinopril long-term to manage blood pressure and heart conditions. Regular monitoring by your healthcare provider is essential.
Conclusion
Understanding the side effects of Lisinopril side effects is crucial for safe and effective use. While most side effects are mild and manageable, being aware of the more serious ones can help you take prompt action if needed. Always consult your healthcare provider with any concerns and regularly monitor your health to ensure the best outcomes.